美国泌尿外科学会(AUA)报告美国肖氏反射弧手术三年结果



【这是新闻发布会前和朋友的通信:附上AUA年会3年结果(先不要对外透漏)。专业数据非常好,比预期的还好。另外,你们结合UROLOGY Times的报道,就会明白美国的手术难度比中国大得多,其中4个人做了神经移植。术前我就对美方和美国病人讲:你们3个做过宫内手术的都需做神经移植,成功的可能最多30%(好了1个半:一个homerun,另一个大便好了),这位37岁的脊髓膨出病人膀胱本来就发育不好,又受损太久,效果难定,其余6位有把握。现在的结果如我所料:总共7人自主排尿,8人自主大便。
另外:肖氏反射弧“消失”及其重要科学意义:
和截瘫不同,在脊膜膨出患者,我在最初20例就观察患儿到最后都无须利用肖氏反射弧排尿,都能像正常人一样意识控制排尿,这我在J.UROL2005文章中已经报告。其实这是肖氏反射弧一个非常重要的科学现象,证明了异类周围神经再生形成肖氏反射弧后能刺激、导致中枢包括大脑的功能重组。我973项目的一项重要内容就是证明这个重组。我已经在20多个SB病人完成了术前和术后获得排尿功能后fMRI研究,证明了这类患者术后在PONS新建立了一个排尿中枢,其位置与正常人不同!中枢的TAKEOVER非常有意思!我在SIU讲座时略微带了一下(你可去看看那视频)。已成文。这项研究非常辛苦不易,历经6-7年 。】
美国泌尿外科学会(AUA)报告美国肖氏手术三年结果(译文)
Tuesday, May 17, 2011 华盛顿 D.C
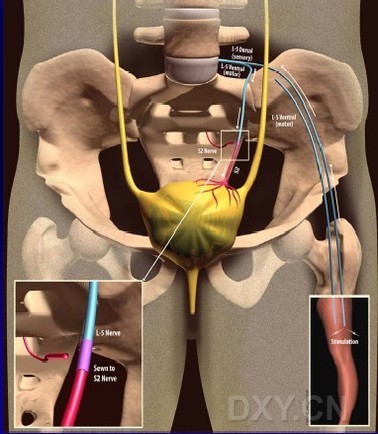
背景和目标:通过显微神经手术吻合腰-骶神经运动支,从而建立皮肤-中枢-膀胱反射弧来重建先天脊柱裂脊膜膨出病人膀胱和肠道功能的理论和手术是肖传国发明的。我们应用此创新手术已3年,现报告结果。
方法:这项为期3年的临床研究计划共收治9位病人(3男6女)平均年龄8岁(6-37岁)。本计划得到伦理委员会批准。经过详尽的术前检查和评估后,为每个病人在神经电生理监控下施行了腰-骶神经通路重建手术(即肖氏反射弧手术---译者注)。术后评估包括随访问卷,尿流动力学测定,排尿日记,肾功能研究和大肠功能评估。
结果:9个病人中,5个曾在出生后24小时内做过脊膜膨出修补手术,3个则在胎儿期用内窥镜作了子宫内脊髓膜膨出修补术,仅一人无手术史。手术平均时间为183分钟(127-278分钟),无任何术中并发症。术后有一个病人发生左足下垂,8个病人出现暂时性小腿肌肉力量减弱(均在6个月左右恢复至术前肌力—译者注:见术后一年报告J.Urol,Peters)。在术后12个月,9个病人中有7个经检测证实已建立皮肤-膀胱反射弧(即肖氏反射弧-译者注)在进行术后第3年随访时,有2位病人没能回访,暂列为失随访。其余7位病人术后3年结果如下:尿流动力学检查证实:膀胱平均容量从210毫升增加到293毫升。7个病人中术前有4个是高反射膀胱,现仅一位还有高反射。平均膀胱顺应性从术前12.2 ml/H2O改善为28.4 ml/H2O,其中3位术前顺应性低于10者(表示逼尿肌基本无功能-译者注)术后变成正常(从7到34.3, 从9.4到21.2, 从8.3到28.4)。 7个病人中,术前仅2人能排出平均23毫升尿,现6人已完全不需导尿管自行排尿,6个病人自己记录每次可排出平均156毫升尿,但尿流率测定证实每次平均排出高达248毫升,残余尿93毫升,有效排尿率为73% 所有6个病人都能排空至少超过59%的膀胱容量。7个病人中,5个需借助些许腹压排尿;7个病人中一个已无尿失禁,6个仍有压力性尿失禁(即打喷嚏或剧烈咳嗽时滴尿,因为尿道括约肌还较弱所致-译者注):其中3个仅偶有滴尿,3个较易滴尿。7个病人中,3个在术前认为自己肠道功能正常,一个没有大便失禁。在术后3年随访时,6个报告肠道功能已正常,4个已无大便失禁。除一位还有高反射膀胱的病人外,其余所有病人都不再需要服用抗胆碱能药物。肾脏B超检查和血肌酐均正常。所有病人均无长期并发症。7个病人中有6个很高兴自己作了本手术。
结论:腰-骶神经改道重建手术(即肖氏反射弧手术-译者注)能够改善先天性脊柱裂脊膜膨出并发神经性膀胱病人的大小便功能。
美国泌尿外科学会(AUA)报告美国肖氏手术三年结果(原文)
Tuesday, May 17, 2011 8:00 AM-10:00 AM
Urodynamics/Incontinence/Female Urology: Neurogenic Voiding Dysfunction
Moderated Poster
Source of Funding: Ministrelli Program for Urology Research and Education (MPURE)
1502: THREE-YEAR CLINICAL OUTCOMES WITH LUMBAR TO SACRAL NERVE
REROUTING IN SPINA BIFIDA
Kenneth Peters
Kevin Feber
Benjamin Girdler
William Nantau
Evan Kass
Jose Gonzalez
Gary Trock
Ananias Diokno
Royal Oak, MI
INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES: The concept of restoring bladder and bowel function in
spina bifida by the creation of a skin-CNS-bladder reflex arc by an intradural lumbar to sacral
motor root microanastomosis was introduced by Xiao. We report our three-year experience with the novel procedure.
METHODS: Nine patients (3 males, 6 females) with median age of 8 (range 6 to 37) years enrolled in this institutional review board approved protocol. After extensive
preoperative evaluation, lumbar to sacral nerve rerouting was performed using intraoperative
neurophysiological monitoring. Postoperative evaluation included follow-up questionnaires,
urodynamic testing (UDT), voiding diaries, renal function studies and bowel assessment.
RESULTS: Of the 9 patients, 5 patients had defect closure within 24 hours of birth, 3 had intrauterine closure and 1 had no prior surgery. Mean operative time was 183 (range 127-278) minutes. No intraoperative complications occurred. One patient developed permanent foot drop and 8 had transient lower extremity weakness. By 12 months, 7 of 9 had a documented cutaneous to bladder reflex. At 3 years, 2 patients did not return for follow-up and were considered non-responders. Seven patients returned for 36-month evaluation. On UDT, maximum cystometric capacity improved from mean 210 cc to 293 cc. At baseline 4/7 had neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO); at 36 months 1/7 had NDO. Median compliance improved from 12.2 ml/H20 to 28.4 ml/H2O and 3 with a baseline compliance of less than 10 had normalization (7 to 34.3, 9.4 to 21.2, and 8.3 to 28.4). At baseline, 2/7 were able to void with an average void of 23 cc. At 36 months, 6/7 no longer required catheterization and 6/7 reported mean voided volume of 156cc on voiding diaries. Uroflow demonstrated a mean voided volume of 248 cc with a 93 cc post void residual and a voiding efficiency of 73%. All 6 patients were voiding > 59% of their bladder capacity. 5 of 7 require some valsalva to void. 6/7 subjects had persistent stress incontinence with 1 subject dry, 3 with occasional leak, 3 frequent leaks. At baseline, 3/7 considered their bowels normal and 1/7 were continent of stool. At 36-months 6/7 considered bowels normal and 4/7 continent of stool. Antimuscarinics were stopped in all subjects except the 1 with persistent NDO. Renal ultrasounds and serum creatinines remained stable. No long-term complications were identified and 6/7 would undergo the procedure again.
CONCLUSIONS:
Lumbar to sacral nerve rerouting can improve bladder and bowel function in patients with
neurogenic bladder associated with spina bifida.
- 上一篇:没有了
- 下一篇:不抛弃、不放弃,这位父亲讲述拯救患儿的心路历程

